A Shahid is NOT a Martyr.
Islamists hijack the use of the word “martyr.” Christianity has many martyrs such as the apostles Stephen and Peter; they were murdered because of their religious beliefs. If a person kidnaps babies and rapes women or blows himself up to kill lots of people because they are unbelievers, he is a suicidal psycho, not a martyr.
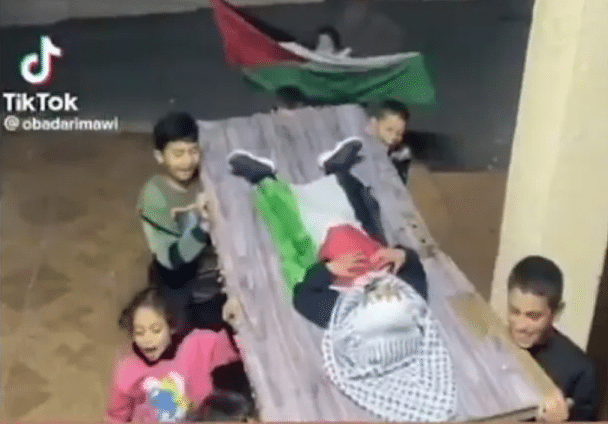

What is a Martyr?
“to put to death for adhering to a belief, faith, or profession”
No one is killing Islamist terrorists because of their beliefs or religion. Democracies around the world are fighting Islamist terrorism and radical Islam, in defense, for survival.
The Civilized Fight Against the Barbaric Radical Islamist Movement
The fight against Islamist terrorism and radical Islam, particularly in the context of self-defense and survival, involves a multifaceted approach adopted by various nations and international coalitions. This approach is primarily driven by the necessity to protect citizens and maintain national security in the face of threats posed by extremist groups.
The Persistent Threat of Islamist Terrorism
Understanding the Enemy
Islamist terrorist groups like ISIS and Al-Qaeda continue to pose a formidable threat to both national and international security. These groups, driven by extremist ideologies, often advocate for violence against a wide range of targets, including Western countries, Muslim communities not aligning with their beliefs, and various other religious and ethnic groups. Their tactics are not limited to terrorist attacks and insurgencies; they also actively engage in spreading propaganda to incite violence and attract new recruits, thereby widening their network of influence and terror.
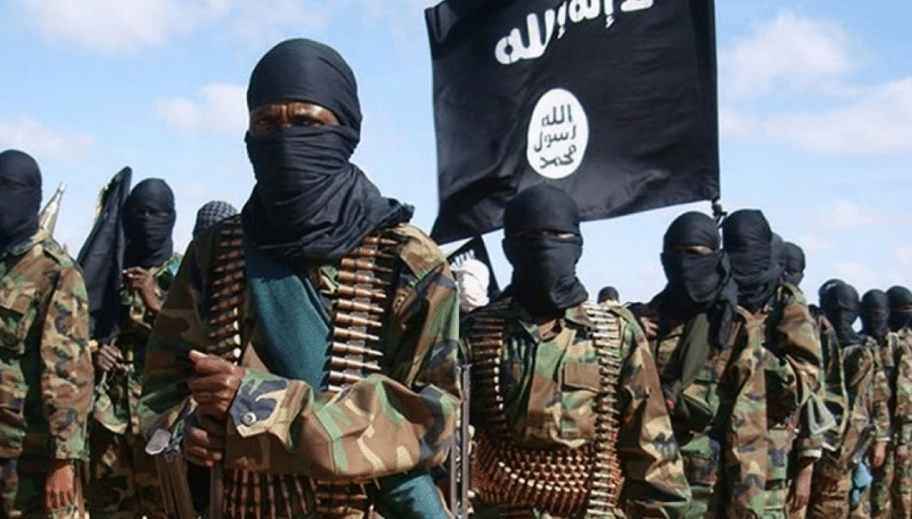

Radical Islam and Antisemitism
Antisemitism among radical Islamist groups is a deeply concerning facet of their ideology, rooted in extremist interpretations of religious texts like the Quran and Hadith, which are used to justify negative portrayals of Jews. These beliefs, which are far removed from mainstream Islamic thought, often merge with historical grievances, particularly those related to the Middle East conflicts, to intensify their antisemitic rhetoric.

Radical Islamists also engage in spreading conspiracy theories, accusing Jews of various global manipulations, to fuel hatred and violence against Jewish people and communities. This form of antisemitism has serious global and regional repercussions, not only exacerbating political tensions in the Middle East but also contributing to worldwide intolerance and terrorism targeting Jews. Addressing this issue poses a significant challenge for counterterrorism efforts, requiring strategies beyond security measures, including educational and community engagement initiatives, and de-radicalization programs.
Combating Terrorism: Military and Intelligence Efforts
The response to these threats is multifaceted. Countries around the globe, often faced with direct threats or attacks, have resorted to military operations. These include strategic airstrikes, ground combat missions, and specific operations aimed at dismantling terrorist infrastructures and neutralizing key terrorist figures. The role of intelligence in these operations cannot be overstated. Intelligence agencies are at the forefront of identifying potential threats, monitoring terrorist activities, and intercepting plans before they come to fruition. This proactive approach is essential in pre-empting attacks and ensuring national safety.

Legal Systems in the Fight Against Terror
In parallel to military and intelligence strategies, democracies are leveraging their legal frameworks to address the menace of terrorism. This encompasses the arrest and prosecution of individuals linked to terrorist activities, disrupting the financial networks that fund terrorism, and implementing laws that impede the operational capabilities of these terror groups. These judicial measures are a testament to the commitment of democracies to fight terrorism within the bounds of law and order.
Global United Front Against Terrorism
Collaborative Efforts for a Safer World
The fight against Islamist terrorism is not confined to national boundaries but is a global challenge necessitating international cooperation. Nations are increasingly sharing intelligence, conducting joint military operations, and offering mutual support in counterterrorism efforts. Organizations such as the United Nations and NATO play pivotal roles in orchestrating these efforts, reflecting a global consensus on the need to confront and dismantle terrorist networks.
Preventing Radicalization: A Proactive Approach
Acknowledging that military and legal actions alone are insufficient to eradicate the threat of terrorism, there’s a growing focus on preventing radicalization. Countries are investing in community engagement initiatives, educational programs, and strategies to counter extremist online propaganda. These efforts aim at addressing the root causes of radicalization, offering a more sustainable solution to the problem of terrorism.
Balancing Act: Security and Human Rights
Navigating the Complexities of Counterterrorism
The campaign against Islamist terrorism is fraught with challenges and criticisms. A significant concern remains the protection of human rights and civil liberties in the process of combating terrorism. Strategies need to be calibrated to ensure they do not inadvertently harm or alienate Muslim communities or lead to collateral damage in military operations. Moreover, the effectiveness of these strategies in fostering long-term peace and stability remains a topic of intense debate.

Striking a Balance
At the heart of democratic responses to terrorism is the crucial balance between ensuring security and upholding individual rights. This balance is imperative in maintaining the core principles of democracy and preventing the erosion of civil liberties. The ongoing fight against Islamist terrorism, thus, is not just about wielding military might or enforcing laws; it’s equally about safeguarding the democratic values and human rights these nations are committed to protect.

